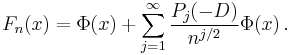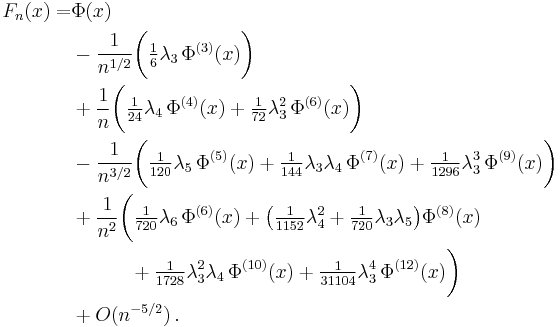Edgeworth series
The Gram–Charlier A series (named in honor of Jørgen Pedersen Gram and Carl Charlier), and the Edgeworth series (named in honor of Francis Ysidro Edgeworth) are series that approximate a probability distribution in terms of its cumulants. The series are the same; but, the arrangement of terms (and thus the accuracy of truncating the series) differ.
Contents |
Gram–Charlier A series
The key idea of these expansions is to write the characteristic function of the distribution whose probability density function is F to be approximated in terms of the characteristic function of a distribution with known and suitable properties, and to recover F through the inverse Fourier transform.
Let f be the characteristic function of the distribution whose density function is F, and κr its cumulants. We expand in terms of a known distribution with probability density function 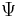 , characteristic function
, characteristic function 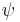 , and cumulants γr. The density
, and cumulants γr. The density 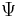 is generally chosen to be that of the normal distribution, but other choices are possible as well. By the definition of the cumulants, we have the following formal identity:
is generally chosen to be that of the normal distribution, but other choices are possible as well. By the definition of the cumulants, we have the following formal identity:
By the properties of the Fourier transform, (it)rψ(t) is the Fourier transform of (−1)r Dr 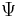 (x), where D is the differential operator with respect to x. Thus, we find for F the formal expansion
(x), where D is the differential operator with respect to x. Thus, we find for F the formal expansion
If 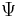 is chosen as the normal density with mean and variance as given by F, that is, mean μ = κ1 and variance σ2 = κ2, then the expansion becomes
is chosen as the normal density with mean and variance as given by F, that is, mean μ = κ1 and variance σ2 = κ2, then the expansion becomes
By expanding the exponential and collecting terms according to the order of the derivatives, we arrive at the Gram–Charlier A series. If we include only the first two correction terms to the normal distribution, we obtain
with H3(x) = x3 − 3x and H4(x) = x4 − 6x2 + 3 (these are Hermite polynomials).
Note that this expression is not guaranteed to be positive, and is therefore not a valid probability distribution. The Gram–Charlier A series diverges in many cases of interest—it converges only if F(x) falls off faster than exp(−x2/4) at infinity (Cramér 1957). When it does not converge, the series is also not a true asymptotic expansion, because it is not possible to estimate the error of the expansion. For this reason, the Edgeworth series (see next section) is generally preferred over the Gram–Charlier A series.
Edgeworth series
Edgeworth developed a similar expansion as an improvement to the central limit theorem. The advantage of the Edgeworth series is that the error is controlled, so that it is a true asymptotic expansion.
Let {Xi} be a sequence of independent and identically distributed random variables with mean μ and variance σ2, and let Yn be their standardized sums:
Let Fn denote the cumulative distribution functions of the variables Yn. Then by the central limit theorem,
for every x, as long as the mean and variance are finite.
Now assume that the random variables Xi have mean μ, variance σ2, and higher cumulants κr=σrλr. If we expand in terms of the unit normal distribution, that is, if we set
then the cumulant differences in the formal expression of the characteristic function fn(t) of Fn are
The Edgeworth series is developed similarly to the Gram–Charlier A series, only that now terms are collected according to powers of n. Thus, we have
where Pj(x) is a polynomial of degree 3j. Again, after inverse Fourier transform, the density function Fn follows as
The first five terms of the expansion are[1]
Here, Φ(j)(x) is the j-th derivative of Φ(·) at point x. Blinnikov and Moessner (1998) have given a simple algorithm to calculate higher-order terms of the expansion.
References
- ^ Weisstein, Eric W., "Edgeworth Series" from MathWorld.
Further reading
- H. Cramér. (1957). Mathematical Methods of Statistics. Princeton University Press, Princeton.
- D. L. Wallace. (1958). "Asymptotic approximations to distributions". Annals of Mathematical Statistics, 29: 635–654.
- M. Kendall & A. Stuart. (1977), The advanced theory of statistics, Vol 1: Distribution theory, 4th Edition, Macmillan, New York.
- P. McCullagh (1987). Tensor Methods in Statistics. Chapman and Hall, London.
- D. R. Cox and O. E. Barndorff-Nielsen (1989). Asymptotic Techniques for Use in Statistics. Chapman and Hall, London.
- P. Hall (1992). The Bootstrap and Edgeworth Expansion. Springer, New York.
- S. Blinnikov and R. Moessner (1998). Expansions for nearly Gaussian distributions. Astronomy and astrophysics Supplement series, 130: 193–205.
- J. E. Kolassa (2006). Series Approximation Methods in Statistics (3rd ed.). (Lecture Notes in Statistics #88). Springer, New York.
![f(t)=\exp\left[\sum_{r=1}^\infty(\kappa_r-\gamma_r)\frac{(it)^r}{r!}\right]\psi(t)\,.](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/17cb04c07411201d0f02f17f70a20b3b.png)
![F(x) = \exp\left[\sum_{r=1}^\infty(\kappa_r - \gamma_r)\frac{(-D)^r}{r!}\right]\Psi(x)\,.](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/87860f6b9db3fc6038457a3b4574c7c5.png)
![F(x) = \exp\left[\sum_{r=3}^\infty\kappa_r\frac{(-D)^r}{r!}\right]\frac{1}{\sqrt{2\pi}\sigma}\exp\left[-\frac{(x-\mu)^2}{2\sigma^2}\right]\,.](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/71ccb86ac1caece74420fd6902acc4cf.png)
![F(x) \approx \frac{1}{\sqrt{2\pi}\sigma}\exp\left[-\frac{(x-\mu)^2}{2\sigma^2}\right]\left[1%2B\frac{\kappa_3}{3!\sigma^3}H_3\left(\frac{x-\mu}{\sigma}\right)%2B\frac{\kappa_4}{4!\sigma^4}H_4\left(\frac{x-\mu}{\sigma}\right)\right]\,,](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/62643b54c98af902f8daa54efe7a1bef.png)
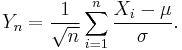
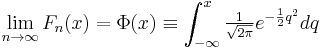
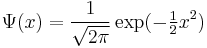
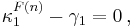
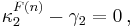
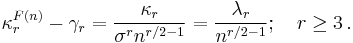
![f_n(t)=\left[1%2B\sum_{j=1}^\infty \frac{P_j(it)}{n^{j/2}}\right] \exp(-t^2/2)\,,](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/a1339a09d05326652d8d843ad7d559ef.png)